In this article, we’ll be comparing DDR4 RAM with DDR5 RAM. We will discuss various aspects, including each memory’s architecture, capacity, channels, and frequency. So, if you’re dilly-dallying between different RAM kits, read on. But first, you might want to check out the following:
These browsers use the least RAM and CPU on Windows. Here’s how to check your RAM’s speed on Windows 11. Want to install more RAM? Here’s how to check the number of available RAM slots in Windows.
What is RAM?
Random Access Memory (RAM) can make or break a computer’s overall performance. It is a type of memory that can be accessed randomly. As such, any byte of memory can be accessed without having to read through all the bytes before it. RAM is much faster than other types of computer memory, such as hard drives and solid-state drives. RAM acts as a temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU (Central Processing Unit) needs to access quickly. This includes the operating system, applications, and data that is being processed. When you open a program, the program’s code and data are loaded into RAM. Similarly, when you save a file, the data is stored in RAM before it is written to a permanent storage device, such as a hard drive or SSD. To simplify it, think of RAM as a buffer between your CPU and your storage drive. The amount of RAM in a computer determines how many programs it can run simultaneously. Additionally, it also dictates how much data it can process at once. A computer with more RAM can run more programs and process data faster than a computer with less RAM.
What is DDR in RAM?
There are various types of RAM. The most commonly used is DDR or Double Data Rate. It is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) that can transfer data twice per clock cycle. As such, it is faster than single data rate (SDR) SDRAM, which can only transfer data once per clock cycle. At the time of writing, the two most common standards are DDR4 and DDR5. DDR4 is the fourth generation while DDR5 is the fifth generation of DDR RAM. Each standard improves upon its predecessor and often brings about new innovations. With the basics out of the way, it’s time to check out the differences between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM.
DDR4 vs DDR5 RAM: Design and Architecture
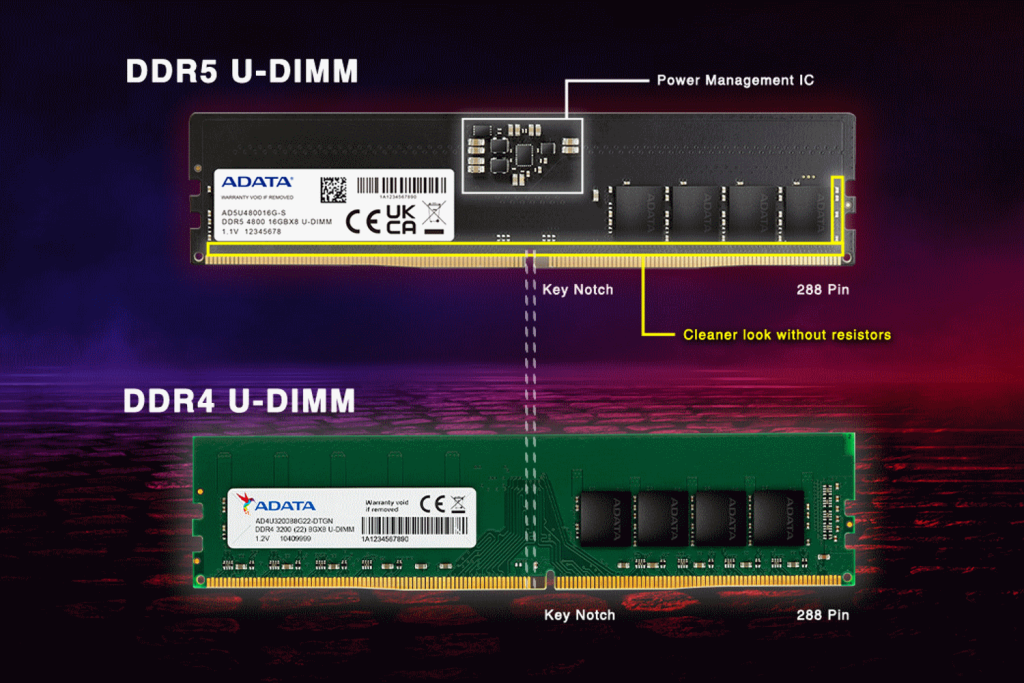
In terms of design, the newer DDR5 RAM looks similar to a DDR4 module. However, DDR4 and DDR5 RAM are backed by different architectures, affecting how they handle and transfer data. Both the RAM standards make use of the same 288-pin connector. However, the pinouts and the position of the notch on each RAM module are different. You should keep an eye out for the same, or you’ll risk installing a RAM module on an incompatible slot. Moving on, DDR4 RAM uses a 4-bit prefetch architecture. On the other hand, DDR5 RAM introduces a new 16-bit prefetch architecture. Without dwelling on too much technical jargon, this change enables DDR5 RAM to transfer larger chunks of data per clock cycle, further enhancing its efficiency and data throughput.
Operating Voltage
Thanks to advancements in tech, DDR5 memory is more power efficient compared to its predecessor. Typically, DDR4 RAM operates at a voltage of 1.2V. On the other hand, DDR5 RAM utilizes a lower voltage, starting from 1.1V. The reduction in operating voltage contributes to improved power efficiency. Furthermore, it also aids in better thermal performance thanks to lower heat being produced. Now, the aforementioned factors might not be of immediate concern to a desktop user. Let’s be honest, you wouldn’t care much if your PC was consuming a bit more or slightly less power. That said, power efficiency and thermals can greatly impact a laptop’s performance. With DDR5 RAM, laptop users can expect better battery backup and improved cooling. It’s worth highlighting that DDR5 RAM comes with a power management controller built into the DIMM. On the other hand, DDR4 RAM relies on the motherboard for power management. By having the controller on the DIMM itself, DDR5 RAM systems can use a simpler power delivery design.
Capacity
Regarding storage, DDR4 RAM modules can be snagged with up to 64GB of memory. On the other hand, thanks to the newer architecture, DDR5 RAM can be outfitted with higher capacities. At the time of writing, DDR5 RAM modules can be configured with up to 256GB of memory. While we currently have 64GB DDR5 kits, higher-capacity DDR5 RAM sticks are just on the horizon. As such, you will soon be able to install more DDR5 RAM as opposed to DDR4 RAM.
Channels
Channels play a pivotal role in determining a RAM’s performance. For the uninitiated, a channel in RAM refers to the number of pathways or lanes available for data to travel between the memory modules and the memory controller. A single-channel mode will use a single data channel, however, there are dual-channel, quad-channel, and octa-channel RAM configurations available too. As far as DDR4 RAM is concerned, each DIMM has a single 64-bit memory channel. Also, it can be configured in single-channel, dual-channel, or quad-channel configurations. The configuration depends on how many sticks you install on your PC, and what configuration is supported by your motherboard. On the other hand, each DIMM of DDR5 RAM has two independent 32-bit channels. As a result, even a single stick of DDR5 RAM works in a dual-channel configuration. Furthermore, DDR5 RAM can be configured in up to octa-channel arrangement, which effectively doubles the memory bandwidth of a DDR5 module when pitted against DDR4 RAM. In the end, channels determine the amount of data that can be transferred simultaneously and directly impact memory bandwidth. More channels are particularly advantageous for memory-intensive tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and gaming.
Frequency
Frequency, measured in megahertz (MHz), represents the speed at which the RAM can transfer data. A higher frequency means data can be transferred more quickly between the RAM and the CPU. DDR4 and DDR5 RAM differ significantly in terms of frequency, which plays a crucial role in determining their performance. Typically, DDR4 RAM operates at frequencies ranging from 2,133MHz to 3,200MHz, which is per the JEDEC (Joint Electron Device Engineering Council) specification. However, there are OEMs that push the DDR4 RAM to higher speeds. In comparison, as per JEDEC, DDR5 RAM is rated from 3,200MHz and beyond. That being said, the slowest DDR5 memory on the market is usually clocked at 4,800MHz. At the same time, buyers will deep pockets will find plenty of DDR5 kits slated at 7,200MHz. And, you can expect this number to go higher as the technology matures.
Compatibility
Clearly, DDR5 RAM brings about a host of improvements. However, before upgrading to the latest standard, it’s worth noting that DDR5 RAM is not backward compatible with DDR4 motherboards. As highlighted in the design section, the notch placement differs on DDR4 and DDR5 DIMMs. As such, it’s vital to ensure that you only buy the RAM standard supported by your motherboard. As such, if you’re using DDR4 RAM and want to upgrade to DDR5 memory, you’ll have to upgrade your motherboard too. Also, unless your CPU has support for both DDR4 and DDR5 RAM, you will likely be in the market for a new processor as well. Pool everything together and you are essentially building a new PC if you choose to upgrade to the newer DDR5 standard.
Pricing and Availability
There was a time when it was quite hard to get your hands on DDR5 RAM. However, things have changed for the better now. At the time of writing, you can easily get your hands on both DDR4 and DDR5 RAM kits. However, since DDR4 RAM has been the dominant standard for several years, it benefits from wider availability and lower pricing compared to DDR5 RAM. While DDR5 is slowly becoming the norm, it is still quite expensive. To put it in numbers, a 32GB (2x16GB) kit of DDR4-3200MHz will cost you roughly $69. On the other hand, a similar DDR5-4800MHz kit will set you back approximately $110.
DDR4 vs DDR5 RAM: Quick Comparison
With all the technicalities out of the way, let us quickly summarize and compare DDR4 vs DDR5 RAM. You can take a look at the handy table below to brush up on the basics.
DDR4 vs DDR5 RAM: Which RAM Is Right for You?
So, is it worth upgrading to DDR5 RAM or not? Well, the biggest deciding factor will undoubtedly be the cost of the upgrade. Not only is DDR5 RAM in itself more expensive than DDR4 RAM, but it also requires newer components. As such, the actual cost of upgrading to DDR5 RAM would depend upon the number of components you need to upgrade alongside it. There’s no denying that DDR5 RAM brings about a ton of improvements. Consequently, if you’re planning to build a new PC, you should invest in the best DDR5 RAM modules on the market to future-proof your investment. As for gamers or casual users, as long as you get optimal performance out of your rig, there’s no immediate reason to upgrade to DDR5 RAM. However, if your current system is being used for work such as video editing, data analysis, or other heavy loads, switching to DDR5 would definitely make things faster. In that case, you must calculate how quickly all the upgrades will pay for themselves. The above article may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. However, it does not affect our editorial integrity. The content remains unbiased and authentic.






![]()





